An Overview of SEARCH Function | Microsoft Excel
Objectives
The SEARCH function locates one string within another string. Then it returns the position of the starting character of the string within another string.
Syntax
=SEARCH(find_text, within_text, [start_num])Arguments
- find_text: Compulsory. It refers to the string you are searching for. The function will return 1 if this value is empty.
- within_text: Compulsory. It refers to the string that you are searching within.
- start_num: Non-compulsory. It refers to the position that you want to start searching from in the “within_text”. By default, this value is set to 1.
Output
Returns the position of the first character of the “find_text” string in the within_text string.
Examples of SEARCH Function
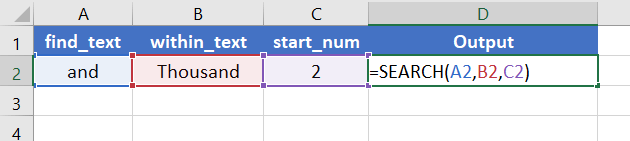
Suppose, you have a string “and” in cell A2. Now you want to search this string within another string “Thousand” in cell B2. To do that you can use the SEARCH function. The formula for this search will be :
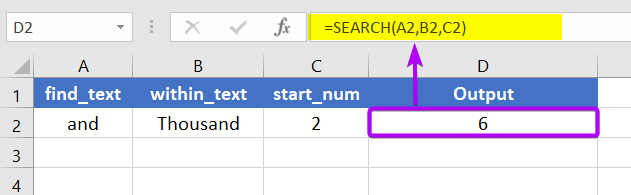
=SEARCH(A2,B2)The output will be 6.
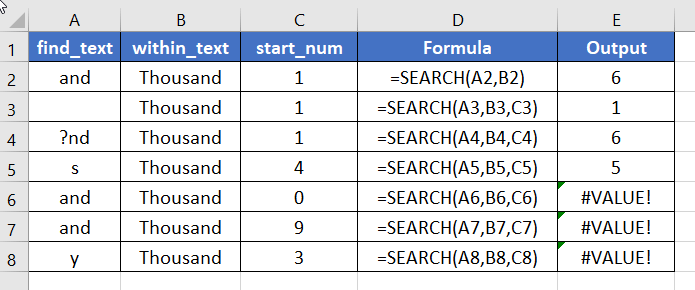
Here are some examples of the usage of the SEARCH function.
Usage Guide of SEARCH Function
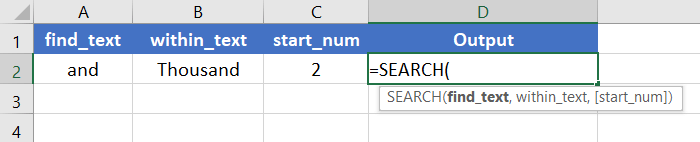
Step_1: Start with inserting an equal sign (=) in a blank cell.
Step_2: Then type SEARCH.
Step_3: Type open parenthesis “(“.
As you type the open parenthesis, Excel shows the syntax of the SEARCH function.
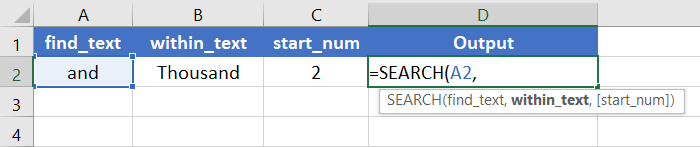
Step_4: Insert a string first.
You can directly insert a string into the function. If you want the string to be and, you have to type and inside a pair of double inverted commas like “an”.
You can also insert a cell address that contains a string.
Here, I’m inserting A2 which has the string and.
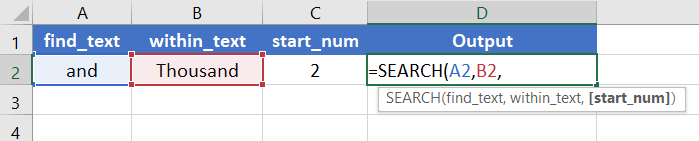
Step_5: Then insert a comma (,).
After inserting the comma, Excel will ask you for the second argument which is the within_text.
Step_6: Now insert the string you want to search within.
You can insert the cell address of the within_text or directly insert a string within a pair of double inverted commas.
Here, the within_text is in cell B2. So, I’m inserting B2 inside the function.
Step_7: Now insert a comma again.
This time Excel will ask you for the third argument which is start_num.
Step_8: Insert a number to specify a position in the within_text. The search will begin from this given position.
Here, I want to start my search with the 2nd character. Thus, I’m inserting C2 which has the number 2.
Step_9: After that, insert the closing parenthesis “)”.
Step_10: Finally, hit the ENTER button to insert the formula inside the cell.
Final Result
The SEARCH function returns 6. Here, the value of find_text is and. So, the first character of find_text is a. The position of a in thousand is 6. As we assigned 2 to the start_num argument, the search started from the 2nd character of thousand which is h. But the count of the position will always start from the 1st character of within_text string.
Availability
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remarks
- The SEARCH function shows #VALUE! error when the start_num value is 0 or greater than the length of the within_text string or if the find_text is not in the within_text
- It returns 1 when the find_text value is empty.
- The SEARCH function is not case-sensitive and supports wildcard characters. ASTERISK(*) matches any sequence of characters and QUESTION MARK(?) matches any single character.
Conclusion
The SEARCH function is one of the text functions in Excel. If you have any questions regarding the SEARCH function, please comment below. Thanks!